Responsibilities
Radiologists are specialist doctors with advanced training in medical imaging and diagnostics. Their primary responsibilities are to establish the underlying diagnosis, assess the results of specific therapies and provide surveillance going forward for a wide range of medical conditions. This requires interpretation of imaging studies, often incorporating a comparison with previous examinations and the production of a detailed report. This is then provided to the referring medical specialist and incorporated into the patient record. The report will usually contain the reason for the examination, the technique employed, the findings and the conclusion and recommendations for further treatment or investigation. Typically, for CT and MRI studies and for plain radiographic (x-ray) examinations the radiologist will not perform the test or operate the equipment, since this is the role of the radiographer. However, for many ultrasound studies, or procedures requiring a radiological ‘intervention’ the radiologist will undertake the procedure themselves.
Education
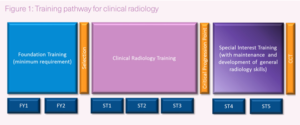
Radiologists are first and foremost medical doctors. They attend medical school to obtain basic medical training and qualifications. In the United Kingdom they will have been required to complete two foundation years in general medical training when they first become a qualified doctor. These foundation years allow doctors to experience a wide variety of varying medical fields before deciding on their chosen medical speciality. Typically, it will require at least 5 years of specialist training to become qualified as a radiologist. During this training they will rotate through all the various subspecialties within the field. As they progress through radiology training, they will learn more advanced skills and techniques. Once they have completed 5 years of speciality training, and have passed the relevant examinations, they will be permitted to enter the register of accredited radiologists and apply to be a consultant radiologist.