Dr Justin Garner
Respiratory Physician
Specialist expertise: COPD, Lung Cancer, Lung Nodules, Interventional Bronchoscopy, Respiratory Medicine, Lung Health.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person.
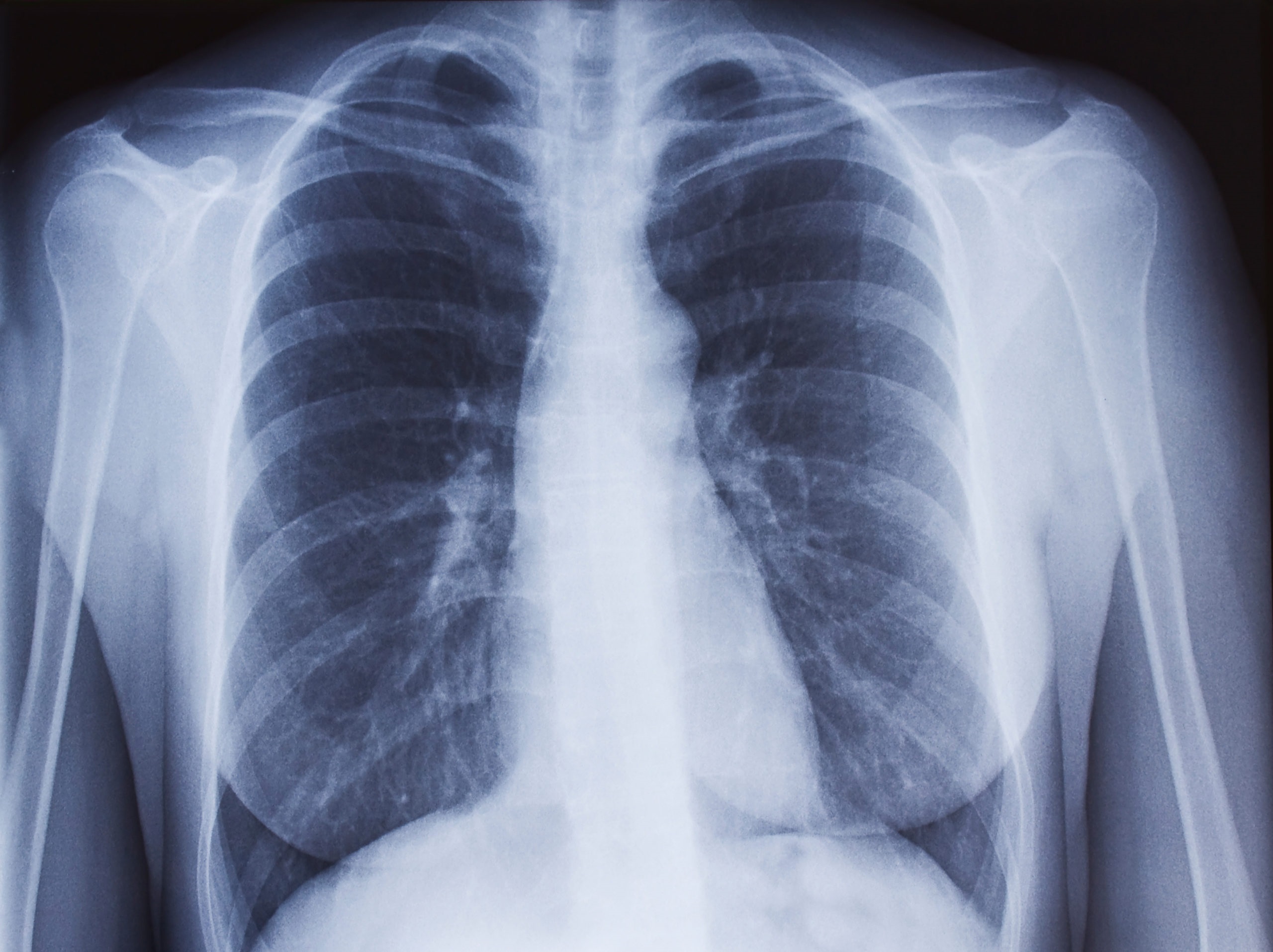
Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by a slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Active TB disease can occur weeks, months or years after you are infected by breathing in the TB bacteria form an infectious person.
In most people, despite inhaling the TB bacteria, the immune system controls the TB bacteria which remains in the body in a dormant state, is not contagious and never causes symptoms. This is called latent TB.
However in about five to ten out of every 100 people with latent TB, the bacteria can start to multiply again or reactivate and lead to symptoms of active TB. This is called active TB disease.
Tuberculosis can affect any part of your body, not just the lungs. In the UK, just over half of people with active TB have TB in their lungs. Tuberculosis can affect other parts of your body such as the lymph glands, bones, gut, kidney or brain.
Symptoms of active Tuberculosis include:
You have a higher risk of developing active TB if:
Active Tuberculosis disease is treated with a combination of antibiotics for 6 months.
Latent Tuberculosis infection can be treated with a preventative course of antibiotics in those with a higher chance of progression to developing active Tuberculosis disease
Currently selected day
Available consultations
Causes
Symptoms
Cough lasting longer than 3 weeks, unexplained w...
Treatments
Medication, Antibiotics
We’ve invited the UK’s best respiratory specialists to join us as partners, with the freedom to make design and delivery decisions based on what’s best for patients.