Dr Abha Gulati
Consultant Dermatologist
Specialist expertise: Skin Cancer, Moles, Eczema, Psoriasis, Acne, Rosacea, Dermatology.
Psoriasis is a common autoimmune skin condition that causes red, scaly patches of skin.
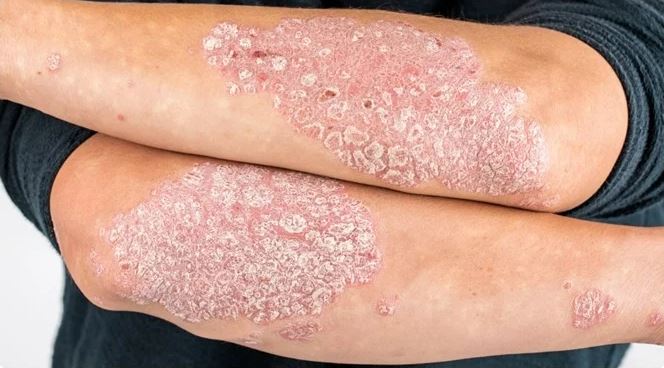
Psoriasis is a long-term chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes red, thick, flaky patches called plaques to develop on the skin. Often, these areas of skin are covered in thin silvery-white scale which can cause itching.
Most often, psoriasis affects the elbows, knees, scalp and lower back, but patches can develop on any area of the body. It’s a very common skin condition and affects men and women equally. Anogenital psoriasis is a specific type of psoriasis in the pubic area. The condition tends to develop between the ages of 20 and 30, and 50 and 60 years old, but can start at any age.
Meet one of our experts
There are several types of psoriasis, and symptoms can vary widely from person to person. Symptoms of the most common form, plaque psoriasis, include:
Usually, skin cells regenerate every 28 to 30 days. With psoriasis, the immune system goes into overdrive causing new skin cells to be produced every three to four days. As these new skin cells move to the skin’s surface they build up to form plaques. Why the immune system behaves in this way isn’t fully understood.
The condition can run in families but the role of genetics as a possible cause of psoriasis is unclear. Psoriasis is not contagious.
A number of factors can trigger psoriasis flare-ups:
Psoriasis is diagnosed by examining the skin. In some cases, a small biopsy or swab may be done to confirm a diagnosis and check for infection.
While psoriasis cannot be cured, flare-ups can be minimised by:
moisturising skin - regularly apply emollients to keep skin hydrated
avoid triggers - identify and steer clear of factors that worsen symptoms
manage stress - implement stress-reduction techniques
healthy lifestyle - maintain a balanced diet and regular exercise
If left untreated, psoriasis can lead to:
psoriatic arthritis - joint inflammation associated with the skin condition
infections - skin infections due to a compromised skin barrier
emotional impact - depression and anxiety due to visible symptoms
cardiovascular issues - increased risk of heart disease
There are several treatments available to relieve symptoms:
At Welbeck, our dermatologists are experts in their field and are dedicated to providing world-class care to every patient.
With access to colleagues across other specialities, our consultants are also able to refer within the Welbeck ecosystem if needed to ensure you receive the best possible treatment as quickly as possible, all under one roof.
All appointments, testing, treatment, and follow-up appointments take place within our state-of-the-art facilities, enabling us to deliver accurate diagnostics and advanced treatments.
Get in touch today to book an appointment. Your health is important to us, so we strive to offer same-day appointments whenever possible.
Our consultants are recognised by the major health insurance companies. If you have private health insurance, your treatment at Welbeck can begin once you have obtained authorisation. We also provide care to self-paying patients. Learn more about the different payment options at Welbeck.
While what causes the immune system to go into overdrive isn’t fully understood, the sudden development of psoriasis is thought to be due to a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers such as infections, skin injuries, stress, certain medications, and smoking.
While scratching does not cause psoriasis to be spread from person to person, it can cause injury to your skin, which may worsen your symptoms or cause the condition to spread to previously unaffected areas of skin. This is known as the Koebner phenomenon.
When psoriasis affects the scalp, it can cause hair loss. This is due to a combination of inflammation in the skin, which causes the hair follicles to become weak and brittle, and scratching due to the itchy, dry plaques.
As psoriasis plaques begin to heal, you’ll likely notice that your skin feels less itchy and is less flaky. You may also see a reduction in redness and a more even skin tone.
Currently selected day
Available consultations
What is psoriasis?
What are the symptoms of psoriasis?
Phototherapy, topical treatments
What causes psoriasis?
Stress, skin injuries, cold dry weather
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
How to prevent psoriasis flare-ups
Complications of psoriasis
What are the treatment options for psoriasis?
Why choose Welbeck?
Book your private consultation
FAQs